What’s involved in creating an LBS lesson that flows?
A Literacy and Basic Skills (LBS) lesson is a narrow, yet revealing window into the complexities, challenges, and rich opportunities so much a part of teaching adult learners who also are aiming to strengthen their digital skills. Whether you are teaching fully online, delivering instruction through a hybrid model, or are fully back in a physical classroom, planning an engaging lesson where skills are honed, connections are made, and a meaningful use of digital technologies is applied, is likely what you aspire to.
During the session, we shared how the Planning a Lesson (PAL) working group came together and explored the intricacies of lesson planning by considering the on-the-ground realities of teaching LBS learners and integrating technology whenever possible. Learn how we met regularly to discuss and identify the common challenges practitioners face before a lesson begins, during the lesson itself, and after a lesson, and how the insights we shared and the tasks we reflected on became the foundation for co-developing resources aimed at bringing flow and deeper learning into lesson planning.
Some tips and lesson planning resources were shared and a sneak peek into the Planning a Lesson website that houses the PAL resources.
Presenters

With twenty-five years of experience supporting adult learners along their unique learning journeys, Olga led the Planning a Lesson (PAL) project drawing on her skills as a seasoned community-based LBS practitioner, an ESL instructor, a vocational counsellor, and an adult education researcher. Her commitment to good teaching that respects adult learners and the real-world skills they bring to their own learning, coupled with her passion for practitioner collaboration and innovation is what set the stage for the PAL project.
Olga is thrilled to have facilitated the working group discussions which were fertile ground for the co-creation of the PAL suite of resources. The working group’s robust teaching experiences, keen insights, diligence, and thoughtful considerations resulted in the co-development of resources that the LBS field will be able to use in order to enhance digital delivery as they engage learners through the lens of purposeful digital integration.

Georgina has worked in adult education (mostly LBS as well as ESL) since 2010. Prior to that, she was an elementary teacher. Georgina is an LBS Instructor with the Ottawa Catholic School Board. She has designed and taught a variety of courses including employment programs, computer skills and academic upgrading.

Joe is an Ontario Certified Teacher who has experience working in education both in Ontario and Nova Scotia. He has worked as an instructor in the Adult Learning and Skills Development department with the Ottawa Catholic School Board (OSCB) since 2022. Joe has taught computer skills, employment preparation, and life skills and has facilitated a remedial class for learners taking online high school credit courses. He currently delivers the Virtual Academic Upgrading course in the OCSB Adult Learning and Skills Development program and also teaches high school.

When John is not in front of his computer taking care of his adult learners at The Literacy Group (TLG) Cambridge location, he is waiting for the day when he can take his twin granddaughters out for a ride on his motorcycle with their Papa John and then curl up on the couch and watch the New York Giants football game on TV.

Leila is a dedicated educator at PTP Adult Learning and Employment Programs with a profound passion for teaching adult learners. With a diverse background spanning several years teaching ESL internationally, she has developed a deep understanding of cross-cultural communication and seeks to empower learners with the skills and confidence to navigate the digital world.

Smita started her teaching career in England in 2009 as an Adult ESL instructor and then continued as a Functional Skills instructor until 2016 where she used technology synchronously in her classes to make the teaching topics more interesting and engaging. As part of her teaching duties, Smita designed Schemes of Work, prepared lesson plans, assessment plans, and assessment activities. Currently, Smita works as an LBS instructor at the Toronto District School Board (since 2017), and also teaches Microsoft Office workshops.
Other resources
What is PAL?
The Planning a Lesson website — PAL for short — is a lesson planning companion that’s a little like a conversation with a teaching peer—a peer who has already thought about planning engaging lessons that flow.
The ideas and materials in this digital space stem from thoughtful questions, robust discussions and the collaborative efforts of the PAL working group. Thus, PAL is a space to engage with the insights from front-line LBS practitioners just like you, and to garner some handy tips.
PAL could also be used as a place to return to for inspiration or to spark discussions around learner-centred approaches and strategies with LBS colleagues.
PAL is
- A new way to look at lesson planning
- An opportunity to reflect on your practice
- A space for front-line insights, tips and resources
You will find a blended-learning lesson planning flow developed for and by literacy practitioners grounded in research and research-in-practice. It is kitchen tested but flexible enough that you can add your own flavour and refine the process to meet the needs of your evolving practice.
PRE-LESSON:
Anticipating challenges
- Challenges to lesson flow present themselves before the lesson even begins. Technology issues and day-to-day class logistics can impact a lesson.
- Consider the most common pre-lesson challenges that can become bottlenecks to flow and try to turn them into learning opportunities.
THE LESSON:
Planning for learning and lesson flow
- Skills are honed not only through discrete tasks, but through active learning strategies and lesson components that build upon each other for connections to be made.
- Take a look at planning a lesson where adult learners work with digital tools and each other by way of activities that are purposefully planned.
POST-LESSON:
Taking the learning beyond the class session
- Taking the learning and newly acquired digital skills into the real world, post-lesson, is a way for adult learners to solidify their learning.
- Explore some simple ways to encourage learners to think about their digital wins and reflect on how to apply their new skills beyond the LBS classroom in a meaningful way.
Two years ago, AlphaPlus organized an advisory group to explore Open Educational Resources (OER) and establish criteria to build a collection for the field. The result is hundreds of FREE units, courses and instructional support materials (with more items being added) that you can use for reading, writing and math instruction, in addition to specific topics of interest to adult learners.
During the session we introduced the collection and demonstrated how it fills a gap, looked at a few example resources that rival paid resources and discussed priorities for adapting and modifying specific resources for your use in online and in-person settings.
Presenters
Christine Pinsent-Johnson
Policy and Research Specialist – Education and Technology at AlphaPlus
With over three decades of experience in the adult learning sector, Christine has a robust understanding of the circumstances hindering learning opportunities and access, and the impact of effective adult learning-based policies and programs. She has been a literacy volunteer, tutor coordinator, computer and classroom instructor, curriculum developer and assessor in school board and community adult literacy programs..
As an organizational development consultant, Christine applies her understanding of system dynamics, learner experiences, accountability processes and metrics, and pedagogy to support equitable and relevant learning opportunities. An experienced researcher, she also draws from evidence-based insights for initiatives, including an understanding of digital disparities in Ontario and Canada and the development of blended learning approaches.
Guylaine Vinet
Organizational Development Specialist – Education and Technology
For more than 20 years, Guylaine has worked in the adult literacy sector. Beginning her career as a librarian supporting literacy practitioners in the deaf and francophone communities, she now assists LBS organizations and practitioners in evolving their knowledge and application of technology and learning using coaching, team training and resource sharing.
As an organizational development specialist, Guylaine provides service in French and English, specializing in information and cloud content management, curating learning resources, learning with tablets and mobile devices and technology problem-solving. Her areas of interest and professional development include online privacy and safety as well as assistive technology and information management.
In her collaborations with LBS organizations as a technology consultant, Guylaine supports teams and educators to build their online resource collection, better understand digital privacy safety and best practices and manage websites and content.
ADDITIONAL RESOURCES MENTIONED BY PARTICIPANTS
- CAEC/GED Practice Test
- Avenue and Tutela are websites that have citizenship resources for ESL learners
OER RESOURCES LIKED/MENTIONED BY PARTICIPANTS:
- CTRL-F
- ESL BITS
- “Writing on the Run looks good”
- “BC Open collection looks amazing, especially resources for the trades”
- “I like Core Vocabulary Word Pictures….has visual and simple words…”
Differentiated learning is an approach that offers opportunities for learners to customize a learning pathway to meet their learning needs, aspirations and preferences.
It can also empower learners to show what they know in different ways.
Learners are provided with multiple options for taking in information, making sense of ideas, and expressing what they learn.
Flexible learning is at the heart of differentiated instruction. Instructors design activities to meet the needs and capabilities of each learner or group of learners. If learners are working in groups, they might not be in the same group for every part of the lesson.
In differentiated instruction, instructors can support learner agency, confidence and independence by:
- scaffolding instruction so that all learners experience success.
- building on learner interests and skills to increase motivation.
- providing opportunities for appropriate learner choice and independent learning.
- helping learner to build a personalized repertoire of strategies to organize information, make sense of ideas, communicate clearly, and retain and retrieve information, concepts and ideas.
- providing frequent opportunities for learner to set goals, reflect on their own learning and develop self-monitoring and self-assessment skills.
Disinformation is false information or information that distorts reality. Disinformation is intended to manipulate public opinion. Most of the time, it is transmitted through mass media or social media. There are several causes for the spread of false information and these can have serious consequences. Disinformation can affect citizens of all ages and education levels. There are ways to reduce the spread of disinformation.
We often hear questions from literacy practitioners about how to embed digital skills in literacy learning when working with learners who have emergent literacy and/or digital skills. They are looking for ways to support learners who may find it challenging to “catch up” on digital skills independently.
We recommend an integrated, blended learning approach. We recommend the learning cycle that we use to teach other literacy skills where making meaning is the primary goal.
When we refer to foundational digital skills or computer basics, we are not talking about skills people need to learn before they engage in technology-rich learning environments and blended learning but the skills and strategies that people might need at different places in the learning cycle in order to complete communication, collaboration and creative tasks and to access resources and services.
Download this resource to reflect on a digital-skills learning cycle and find a collection of places that support learners with beginner literacy skills who want to learn more about using digital devices and connectivity for learning.
After searching over 100 resources collections and lists from Canada, the U.S., U.K. and Australia, we have developed a fully vetted collection of workbooks, modules and activities that address a range of instructional topics in our Open Educational Resources and Instructional Materials Collection.
To build the collection, Christine and Guylaine assembled a group of instructors from school boards and community groups, representing urban and rural communities across the province. Members work in program areas ranging from workforce development to academic, with diverse learner groups. They provided guidance to ensure the materials are
- Free and ad-free
- Shareable and reproducible
- Mostly modifiable for use in different formats and to change content
- Ready-to-use with instructional activities
- Accompanied by tips, ideas and strategies for educators to implement.
Take some time to explore the collection. You’re sure to find some gems that you can use right away.
Learn how to use Google Slides to create activities that learners can do alongside each other individually or in groups.
Check out the presentation below to see how. Click on the full screen icon (two arrows) in the bottom right corner to see a larger version.
To find templates for creating collaborative workspaces in Slides, check out the collection at Ditch that Textbook: ditchthattextbook.com/resources/templates
If you’d like to learn more about using Google slides as a collaborative workspace or schedule a demonstration, contact Tracey or our Quick Tech Help service.
Jamboard (Jamboard Tip Sheet) will be discontinued on December 31, 2024. Using Google slides this way is a possible alternative. In the Sample Jamboard folder you can see activities by some Ontario literacy practitioners (and me) that you can copy and adapt to the Google slides method.
You will also see a folder called EDTechTeacher Samples where you will find copies of many of the Jamboards that were shared in the shared in the Building digital skills with Google workshop.
You might have heard about MTML’s smartphone learning modules but we want to go a bit deeper to explore how they are applied in the literacy field and what other programs are doing when it comes to using smartphones with their learners. In this showcase, we explored the modules and discussed how smartphones are changing the way we learn, teach and use technology on a daily basis.
Presenters
Metro Toronto Movement for Literacy
Also known as MTML, is a network of organizations and individuals supporting adult literacy in Toronto and York Region.
Ambreen Ahmad, Managing Director
Ambreen has 20 years of experience in the education field. Possessing a Masters in English Literature and in Educational Planning and Management, she has maintained successful positions as a Vice Principal, English Language Instructor, Manager HR, Communication Executive and Literacy practitioner.
Currently, she is working as a Managing Director at Metro Toronto Movement for Literacy, a non-profit organization that supports adult literacy in Toronto and York Region. Her previous work experience and life-long learning certificates and diplomas bring a wealth of information to develop learning strategies, recruitment procedures and governance.
Her dedication and determination in helping individuals grow and develop are highlighted in all her professional achievements. She is also passionate about volunteering and has been an ardent volunteer in many non-profits across GTA. She loves to cook and paint in her free time.
LAMP Adult Learning Program provides a foundation to the first step back to learning, with a strength based community approach. Learners achieve health and well being, develop independence, further education for training and employment needs. They focus on personal goals of health, civic engagement, social inclusion, and quality of life. Learners improve their reading, writing, and/or digital literacy (smartphone, ipad and laptop/desktop) skills in our community-based literacy and basic skills program.
Johanna Milic
Program Supervisor
Leads creative development and collaboration with Support Organizations and
in programs at LAMP.
Anita Dhanjal
Community Literacy Worker
Digital and Computer, Reading and Writing Instructor.
Robert Connelly
Community Literacy Worker
Digital and Computer, Reading and Writing Instructor.
Literacy Council York Simcoe (LCYS)
The Skills Upgrading Center provides customized training programs and job-specific workshops to assist adults in York-Simcoe in improving their employment prospects, preparing for a higher education, and acquiring the skills they need for a successful future.
Brittany Horlings, Program and Marketing Assistant
ADDITIONAL RESOURCES MENTIONED BY PARTICIPANTS
AlphaPlus OER Library – Mobile Devices
How to scan QR codes on Android Phone
How to scan QR code from an image in gallery
Computer Hope – computer dictionary, terms, and glossary
Connected for Success – Low income affordable plans from Rogers (mobile, internet and TV options)
On November 16, 2023 AlphaPlus hosted our 12th Community Gabfest.
The theme was Games and gambits – keeping learning fun.
We used a Jamboard to guide our conversation: Wayfinders Gabfest 12 Jamboard.
The conversation starter was “What are your favourite games or community building activities to use with learners?”
This gabfest was about the games and activities learners love. We shared our ideas for keeping learners engaged by building community and having fun together.
We started by talking about the games we like and why we like them and then we played a general knowledge Kahoot! that Guylaine had made for us.
We shared some resources:
- Gamified Curriculum from Literacy Link South Central – www.llsc.on.ca/gamification
- Showcase on Games from AlphaPlus – alphaplus.ca/resources/virtual-showcase-should-we-kahoot-it
- Building Community Tip Sheet from AlphaPlus – alphaplus.ca/resources/building-community-in-remote-learning-environments
- Digital Learning Selector from New South Wales Department of Education – app.education.nsw.gov.au/digital-learning-selector (This website provides numerous ideas for active learning and assessment activities with templates you can adapt.)
Then we asked:
What are your favourite games or community building activities to use with learners?
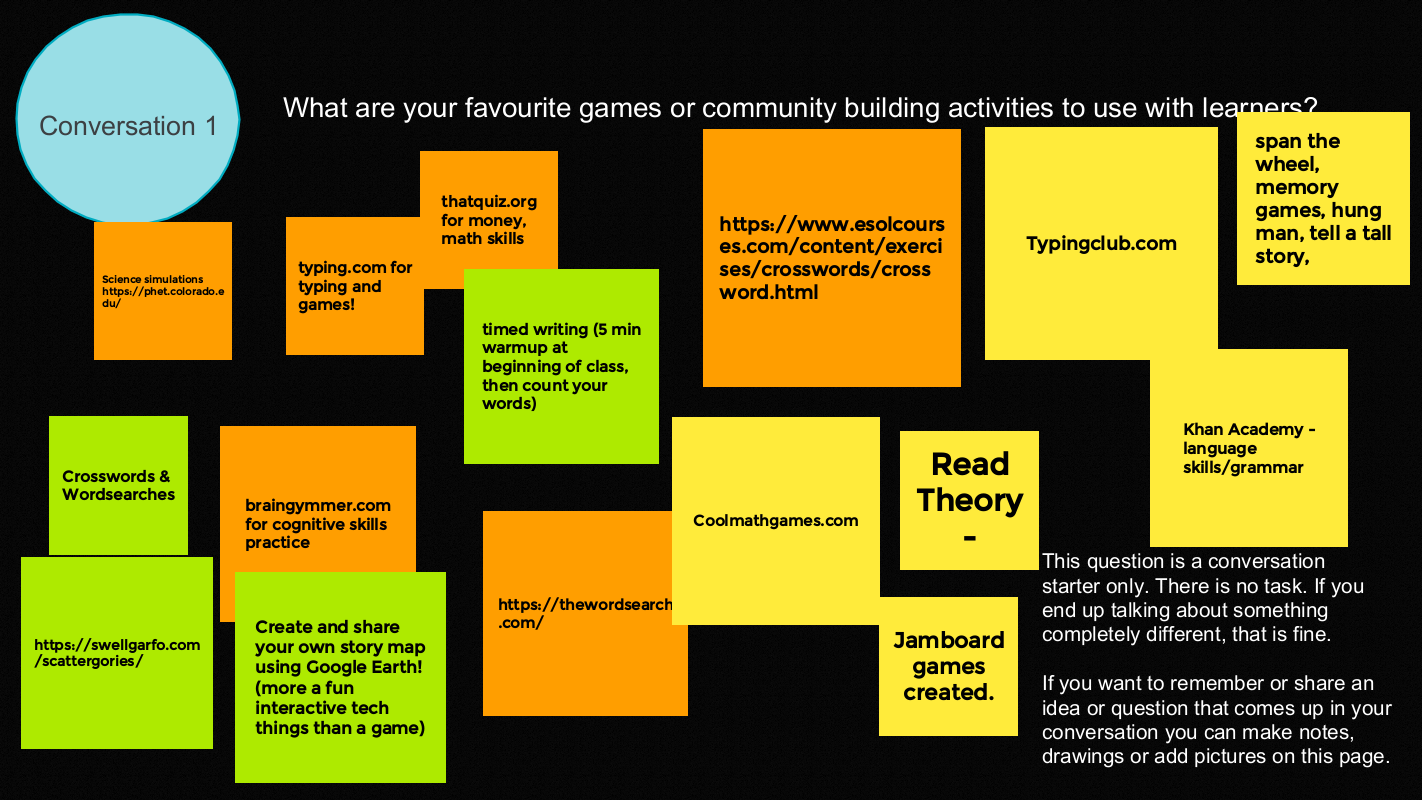
Favourite games and activities
- Create and share your own story map using Google Earth (more a fun interactive tech thing than a game)
- Timed writing (5 min warmup at beginning of class then count your words)
- Spin the wheel, memory games, hang man, tell a tall story.
- Jamboard games –
- Put one letter on a sticky note to spell out a word or phrase. Learners make as many words as they can with the letters.
- More examples here – or at Jamboard Tip Sheet and samples
Language
Crosswords & Wordsearches
- thewordsearch.com
- thewordsearch.com/hangman www.esolcourses.com/content/exercises/crosswords/crossword.html
- swellgarfo.com/scattergories
Math and Science
- phet.colorado.edu (science simulations)
- braingymmer.com
- coolmathgames.com
- thatquiz.org (money and math skills)
Typing
Thank you Gabfesters for your collegiality and for sharing your knowledge and sense of fun.