ChatGPT is a natural language processing tool driven by artificial intelligence (AI) technology that allows you to have human-like conversations and much more with a chatbot. The language model can answer questions, and help you with tasks such as composing emails, essays, and code.
ChatGPT takes online writing tools such as QuillBot to the next level—or the next few levels—by leveraging the knowledge stored on the internet to respond to queries and requests.
ChatGPT is designed to simulate human-like responses to text-based communication.
It is built on an architecture that mimics the human brain called the GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer) model. The GPT architecture allows ChatGPT to generate natural language text that is highly coherent and contextually appropriate.
ChatGPT uses a large database of written text, such as books, articles, and websites, that it has been pre-trained on. When a user inputs a message or question, ChatGPT uses this pre-trained knowledge to generate a response that it believes best answers the question or provides a relevant response to the message.
See some additional resources below and in the ChatGPT Gabfest summary.
Eduaide.AI – specifically for teachers
Perplexity – ChatBot and search engine
Anthropic Claude – an AI workplace assistant
Bing Chat (Microsoft chat bot and search)
ChatPDF
Google AutoDraw
Google Duet AI – for people with access to a Google Workspace account
GrammarlyGO
Microsoft Designer
Microsoft Copilot
Quizlet Q-Chat
Google Gemini
And the controversial AI image generators:
DALL-E 2
Midjourney
Canva: Text to Image or Magic Edit
Padlet: I Can’t Draw
Adobe Firefly
from the Ed Tech Centre @ World Education
Open Prompt Book from CampGPT at the Ed Tech Centre @ World Education: a resource for and by adult educators about how they use AI mostly as a brainstorming tool. As they report, “Over and over again in CampGPT, educators describe the use of chatbots as a great “starting point.” In fact, some find that using these tools is most effective for generating ideas rather than ready-to-use materials.” Here is a description of the Open Prompt Book: “In CampGPT, educators experimented with generative AI-enabled tools like chatbots and image generators to learn and explore together. Their work and insights have been compiled in the Open Prompt Book from CampGPT. Throughout this prompt book, you’ll learn more about generative AI, what educators use it for, and key tips and tricks.”
AI for Learning and Work from the Ed Tech Centre @ World Education: You can find the recordings of the four Generative AI EdTech Bytes that cover the applications and implications of generative AI for education (YouTube Playlist) plus a series of blog posts about the use of ChatGPT and AI in education.
ChatGPT: Leveraging AI to Support Personalized Teaching and Learning in the June 2023 Adult Literacy Education Journal by Sarah Cacicio and Rachel Riggs: a a resource for teachers/instructors with ideas for how to use ChatGPT for learning in an adult literacy setting.
from Contact North
My Digital Companion: Making Sense of ChatGPT from Contact North: a resource for students/learners to help them use ChatGPT safely, ethically and creatively for learning.
Leveraging ChatGPT Instead of Banning from Contact North: a resource for teachers/instructors with ideas for how to use ChatGPT for learning in a college setting.
10 Practical Ways Faculty and Instructors Can Use AI from Contact North
Contact North has a series of recorded webinars on the use of AI in education.
- ChatGPT: Threat or Menace?
- Content Creation Using AI: How AI Can Be Used to Build Courses and Learning Experiences
- ChatGPT, AI and The Future of Teaching and Learning: We All Need a Digital Assistant
- The Generative AI Mirror: The Five Pathologies of EdTech Discourse About New Technologies
- Navigating a World of Generative AI: Suggestions for Educators
- AI in Education: Innovate or Automate? Navigating the Pedagogical Crossroads
from Control Alt Achieve
Super Tutor: AI to Support all Learners from Control Alt Achieve: a 1-hour training video that explores both AI tools (ChatGPT, Google Bard – not currently available in Canada, Diffit, Eduaide, MagicSchoolAI, Brisk, Goblin Tools…) and practical uses (reading, writing, tutoring…) to help support learners. All the resources used in the video are included in a list on the page.
from EdTech Teacher
EdTech Teacher Chat GPT Tips by Tom Daccord: a resource for teachers/instructors with ideas for how to use ChatGPT for learning in a K-12 setting.
- Part 1 – Role-Playing Activities
- Part 2 – Quizzes and Tests
- Part 3 – Personalized Learning
- Part 4 – Teacher Writing Assistant
- Part 5 – Example Generator
- Part 6 – Creating Educational Games
- Part 7 – Language Learning
- Part 8 – Creative Writing
- Part 9 – Summarizing
- Part 10 – Feedback
from Center for the Advancement of Teaching Excellence (CATE) at the University of Illinois
AI Writing Tools by Erin Stapleton-Corcoran, CATE Instructional Designer and Patrick Horton, CATE Instructional Designer (2023)
from Open AI
Teaching with AI: Stories of how educators are using ChatGPT and some prompts to help educators get started with the tool.
As this is an evolving technology, we’ve been updating this page with resources and things we have been learning about ChatGPT and other generative AI tools.
- Generative AI is artificial intelligence capable of generating text, images, or other media – like ChatGPT and the tools listed below. Generative AI grew out of a field of AI study and practice called machine learning.
- Machine learning is a type of AI that uses algorithms trained on data sets to create models that enable machines to perform tasks that would otherwise only be possible for humans. When we put a bunch of these algorithms together in a way that allows them to generate new data based on what they’ve learned, we get a model or an engine tuned to generate a particular type of data. The engine that powers Chat GPT is a large language model.
- Large language models are a type of AI algorithm that use deep learning techniques and large data sets to understand, summarize, generate and predict new content.
People often use the term AI to mean all of these things, one of these things, or something altogether different.
Some guides:
- What Is Generative AI: A Super-Simple Explanation Anyone Can Understand by Bernard Marr at Forbes (September 2023).
- A simple guide to help you understand AI by By the Visual Journalism Team at BBC (July 2023).
- Akinator is a game that shows the questions machines ask to narrow down choices to pinpoint what a searcher is looking for. Think of a character (real or fictional), an animal or an object and answer the questions Akinator asks until it discovers what you are thinking of or gives up. The program sifts through all the data it contains after each response creating narrower and narrower categories until it can come up with a single guess. These are called decision trees.
- To learn more about how data is used to train models, check out Slice of Machine Learning — an interactive tutorial that teaches you how to build a machine learning classification model using a decision tree where you can try to train a computer to identify pizza.
- Quick Draw is a game that shows how AI learns to identify objects. Click Let’s play and try to draw the picture you are asked to draw. The program will try to guess what you are drawing as you go. Once you are finished playing, you are invited to see the ways other creators drew the items and how the program figured out – or didn’t – what you were drawing. You can see the complete data set it is using to make the guesses here: The world’s largest doodling data set. This is how we all contribute to to the AI datasets. We create things, put them on the internet, and programs are sent out to scrape our creations for the data they will use to create the next thing.
Open Prompt Book from CampGPT at the Ed Tech Centre @ World Education: a resource for and by adult educators about how they use AI mostly as a brainstorming tool. As they report, “Over and over again in CampGPT, educators describe the use of chatbots as a great “starting point.” In fact, some find that using these tools is most effective for generating ideas rather than ready-to-use materials.” Here is a description of the Open Prompt Book: “In CampGPT, educators experimented with generative AI-enabled tools like chatbots and image generators to learn and explore together. Their work and insights have been compiled in the Open Prompt Book from CampGPT. Throughout this prompt book, you’ll learn more about generative AI, what educators use it for, and key tips and tricks.”
AI 101 for Teachers – Large Language Model Prompting Guide (slide deck)
ChatGPT Prompts for Teachers: Unlocking the Potential of AI in Education from LearnPrompt.org
GenAI Chatbot Prompt Library for Educators from AI for Education
The Ultimate Prompt Engineering Guide for Text Generation – This site offers a spreadsheet of several hundred prompt examples.
The Prompt Index – a community of prompt engineers is developing an AI prompt database full of prompts for ChatGPT, Bard, Claude 2, Llama, Midjourney, Dalle and Stable Diffusion!
Updates on Generative AI and the use of copyrighted content
Artists are asking for an ethical AI that respects the three Cs: consent, control and compensation. We are all content creators in the age of AI.
Art and AI Regulation : Implications for arts and culture by Valentine Goddard (September 2023)
Recommendations that have been submitted to the Quebec Innovation Council, and to the AI Advisory Council of Canada’s Ministry of Innovation, Science and Economic Development.
Updates on the copyright suits and Open AI
‘Impossible’ to create AI tools like ChatGPT without copyrighted material, OpenAI says by Dan Milmo at The Guardian (January 2024)
“AI companies’ defence of using copyrighted material tends to lean on the legal doctrine of ‘fair use’, which allows use of content in certain circumstances without seeking the owner’s permission. In its submission, OpenAI said it believed that ‘legally, copyright law does not forbid training’.“
‘New York Times’ sues ChatGPT creator OpenAI, Microsoft, for copyright infringement by Bobby Allyn at National Public Radio (December 2023)
“The ‘Times’ is the first major media organization to drag OpenAI to court over the thorny and still-unresolved question of whether artificial intelligence companies broke intellectual property law by training AI models with copyrighted material.
Courts have said fair use of a copyrighted work must generate something new that is “transformative,” or comments on or refers back to an original work — something the Times argues does not apply to how OpenAI reproduces the paper’s original reporting.
‘There is nothing ‘transformative’ about using The Times’s content without payment to create products that substitute for The Times and steal audiences away from it,’ Times lawyers wrote in the suit on Wednesday.“
- Music publishers sue Amazon-backed AI company over song lyrics by by Blake Montgomery at The Guardian (October 2023)
- Sarah Silverman sues OpenAI and Meta claiming AI training infringed copyright by Dan Milmo at The Guardian (July 2023)
- Authors file a lawsuit against OpenAI for unlawfully ‘ingesting’ their books by Ella Creamer at The Guardian (July 2023)
- Another group of writers is suing OpenAI over copyright claims by Emma Roth at The Verge (September 2023)
OpenAI offers to pay for ChatGPT customers’ copyright lawsuits by Blake Montgomery at The Guardian (November 2023)
“The compensation offer, which OpenAI is calling Copyright Shield, applies to users of the business tier, ChatGPT Enterprise, and to developers using ChatGPT’s application programming interface. Users of the free version of ChatGPT or ChatGPT+ were not included.“
Updates on the bias risks of AI
Some people say that using an LLM – large language model – like ChatGPT is like using a calculator but calculators do not show us content that is racist, sexist or homophobic. We can work on our critical thinking skills to adapt to a AI world but what is the benefit of being exposed to this type of content?
These Women Tried to Warn Us About AI by Lorena O’Neil at Rolling Stone Magazine (August 2023)
“Researchers — including many women of color — have been saying for years that these systems interact differently with people of color and that the societal effects could be disastrous: that they’re a fun-house-style distorted mirror magnifying biases and stripping out the context from which their information comes; that they’re tested on those without the choice to opt out; and will wipe out the jobs of some marginalized communities.”
What ChatGPT Tells Us about Gender: A Cautionary Tale about Performativity and Gender Biases in AI by Nicole Gross (June 2023)
“This paper’s central argument is that large language models work performatively, which means that they perpetuate and perhaps even amplify old and non-inclusive understandings of gender. Examples from ChatGPT are used here to illustrate some gender biases in AI. However, this paper also puts forward that AI can work to mitigate biases and act to ‘undo gender’.”
The Pear, You & AI by Valentine Goddard
“The Pear, You and AI is a women-led collaborative annotation initiative, designed as part of a larger project on Algorithmic Art to Counter Gender Bias in AI. In this initial phase, we are undergoing data collection based on your words and perceptions associated with words like women, beauty, imperfection.“
A People’s Guide to Artificial Intelligence by Mimi Onuoha and Diana Nucera a.k.a. Mother Cyborg via Allied Media Projects (PDF)
- What does fairness look like when computers shape decision-making?
- Who is creating the future, and how can we ensure that these creators reflect diverse communities and complex social dynamics?
“This zine, published in August 2018, explores these questions through a series of explanatory text and whimsically illustrated pages that takes the reader on a journey that demystifies the often opaque world of artificial intelligence.“
5 Ethical Implications of AI in Education: A Guideline for Responsible Classroom Implementation
by Luis Pardo (June 2023)
“A responsible AI implementation in a school context begins with careful planning and consideration of all stakeholders’ needs. This involves ensuring that AI tools are accessible and designed to accommodate diverse learning needs, including those of students with Special Educational Needs and Disabilities (SEND). Schools must ensure all students have access to the necessary technology to prevent the widening of the digital divide. The AI tools should be trained on diverse data sets to minimize algorithmic bias and should be designed to offer personalized learning experiences, considering each student’s unique learning pace and style.”
The Artificial Intelligence & Equality Initiative from the Carnegie Council for Ethics in International Affairs
“The Artificial Intelligence & Equality Initiative (AIEI) is an innovative impact-oriented community of practice seeking to understand the innumerable ways in which AI impacts equality for better or worse. We work to empower ethics in AI so that it is deployed in a just, responsible, and inclusive manner.”
AI and education: guidance for policy-makers from UNESCO (2021)
“…while AI might have the potential to support the achievement of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) of the United Nations, the rapid technological developments inevitably bring multiple risks and challenges, which have so far outpaced policy debates and regulatory frameworks. And, while the main worries might involve AI overpowering human agency, more imminent concerns involve AI’s social and ethical implications – such as the misuse of personal data and the possibility that AI might actually exacerbate rather than reduce existing inequalities.”
Update on the use of AI by Canadian students and employees
One in five Canadians using generative artificial intelligence tools from KPMG (June 2023)
“A survey of 5,140 Canadians found 1,052 (20 per cent) have used generative AI to help them do their jobs or schooling. The most common uses include research, generating ideas, writing essays and creating presentations. Respondents say the use of the technology has enhanced productivity and quality, created revenue and increased grades but, in the process, they are engaging in behaviour that could create risks for their employers.”
Updates on the use of AI by Canadian businesses
More than one third of Canadian businesses experimenting with ChatGPT from KPMG (April 2023)
“A majority of Canadian businesses are aware of the risks of having poor quality data, with more than half (54 per cent) admitting they are very concerned their organization might be making decisions based on poorly designed AI algorithms, and yet only 44 per cent regularly retaining independent third-party experts to vet or assess their AI algorithms for errors and bias.”
Automation Nation? AI Adoption in Canadian Businesses from The Dais at the Toronto Metropolitan University (September 2023)
“In all businesses with five or more employees, as of the end of 2021, only 3.7 percent of firms say they had adopted artificial intelligence in any way.”
Canada’s AI imperative – From predictions to prosperity from Deloitte (November 2018)
“Truthfully, there are still many unknowns about general AI’s potential and humanity’s ability to grasp it. But regardless of whether we ever reach the point of general AI, there’s still a clear imperative for a country and its businesses to invest in AI technologies, and to shape the economic and social conditions required to foster their uptake.”
The CommonCraft library of videos is designed to help us introduce and explain complex subjects in about three minutes. Most come with a transcript and lesson plan. Close captioning is available.
Find the transcript for this video here: Generative AI explained by Common Craft
Download a lesson plan
Find the transcript for this video here: Large Language Models (LLMs) AI explained by Common Craft
Download a lesson plan
Find the transcript for this video here: Chatbots and AI explained by Common Craft
Download a lesson plan
A HyperDoc is a digital document—such as a Google Doc—where all components of a learning cycle have been pulled together into one central hub. Within a single document, students are provided with hyperlinks to all of the resources they need to complete that learning cycle.
The Basic HyperDoc Lesson Plan Template from HyperDocs Templates for Getting Started nicely illustrates how a lesson cycle can be incorporated into a hyperdoc.
To help practitioners who are exploring the use of HyperDocs to enhance learner agency, AlphaPlus has a created a website dedicated to the creation and use of HyperDocs in adult literacy where you will find tips and examples.
On May 11, 2023 AlphaPlus hosted our eighth Community Gabfest.
The conversation starter was “What is your favourite blended learning resource? And why?”
We received a suggestion that the Gabfest may be a good place to share ideas for good resources, strategies and tools for blended learning— the kitchen-tested stuff that practitioners find useful and effective in a variety of settings.
We used a Jamboard to guide our conversation: Wayfinders Gabfest 8 Jamboard.
We started by brainstorming what we are looking for in resource recommendations – what elements are important to us.
We asked three questions:
- What are your favourite blended learning (integrated digital and literacy skills) resources?
- What are your favourite digital skills (teaching people digital skills explicitly) resources?
- What are your favourite digital literacy (learning about ethics, privacy and safety) resources?
And here is the list we came up with:
Blended learning
- Copian is the newer name of what used to be called note the National Adult Literacy Database. There was funding in the 90s and into the 2000s for a national database of all the adult literacy resources from across the country. It is now taken care of by CDEACF (Centre de documentation sur l’éducation des adultes et la condition féminine).
- I was working with people who were considering going into the trades. I was using ABC Life Literacy’s UP Skills for Work. They had a section on confidence, but it seemed a little thin. So I went into Copian — there’s lots of writing by learners on Copian — and I found stories by learners, mostly from Atlantic Canada in the 2000s, talking about how they noticed their confidence had changed. We’re incorporating those stories into the activity. It is authentic material by people in adult learning environments. I find that finding learner writing is one of the most powerful ways, no matter what the topic is, to help people to reading or writing or even using it for digital skills.
- Free English News Lessons in 7 Levels – You can read or listen to the news and do activities at the level that works best for you. There is advertising on this site. It is mostly at the top of the page.
Citizen Literacy app (useful for learning disabilities/difficulties, uses a phonetic approach, can use the app on an Android or you can access the lessons on the website)
- I’ve started using this with a learner who’s been in our classes over the years but continues to struggle. She might have an undiagnosed learning disability. It’s fun and uses a phonetic approach, but not in a traditional way.
- The Citizen Literacy Learner web app* is free to use, does not require user registration, has no adverts, no in-app purchases and takes no personal information. Featuring a voice driven interface suitable for low literacy learners with two virtual teachers that provide instruction and instant personalised feedback. It keeps track of each learner’s progress anonymously to provide feedback. Importantly, the design avoids looking like a children’s learning resource – a strongly demotivating factor for older learners. There is multimedia interactivity and gameplay, together with voice and handwriting recognition. Enabling some of the first online independent learning opportunities for low literacy learners. From a standing start, by the end of lesson 2, learners are beginning to read and write simple sentences.
- This is a good tool to change up your intake screening passages for reading. It finds new leveled articles and can discourage dishonesty and sharing of reading passages.
- Google Applied Digital Skills is a free online curriculum created by Google that combines real life skills with Google tools in self-paced, video-based lessons that are perfect for independent, hybrid or remote learning. From creating stories and recipes to researching and developing a topic or managing a budget, the curriculum engages learners in problem solving, critical thinking, and hands-on opportunities to develop skills and knowledge. Applied Digital Skills lessons are similar to real world projects and tasks that learners may encounter at work, in their daily lives and in educational settings .
Teach Online from Contact North
- TeachOnline is a place to find resources about the latest trends, best practices, training opportunities, and teaching resources in online and distance learning under the following categories:
- Pockets of Innovation
- Tools and Trends
- Training and Resources
- Upcoming Conferences
- Webinar Series
Linkedin Learning and Gale Learning
- LinkedIn Learning and Gale are online learning providers. LinkedIn Learning provides video courses taught by industry experts in software, creative, and business skills. Gale eLearning solutions provide teachers, students, and adult learners with online learning resources that include 3D virtual learning; elementary, middle, and high school databases; career training; professional development opportunities; and interactive, industry-specific courses taught by world-class instructors.
- You can access these courses and resources for free in some public libraries.
Virtual reality (e.g. Body swaps – Soft Skills simulations): through Contact North centres, literacy programs can use these tools at no cost
- We have a forklift simulator training and hazardous response. We have access to a program called Body Swaps, which is soft skills, so interviewing, preparation, public speaking, dealing with biases. It puts the person in a virtual reality. at first they are answering questions, but then it flips it and you’re hearing your own response and seeing what your avatar is doing. We’re currently working to look to see what we can find to be able to integrate VR more with LBS providers. We have a centre in Toronto and if you are in our centres using our equipment, there is no cost. We are looking to be able to do some more partnerships with community organizations and things like that.
Maps apps (various ways to use them)
- A learner that is in a senior’s program asked about it. We created a lesson about all the different starting points: for example, if someone sends a text with the address, you can tap on the address in the text. and it will open the maps app. I think the literacy part was helping learners understand that with digital devices there’s always more than one way to do the same thing–even though it’s a skills piece, I think the literacy part was thinking of it like a building with many doors and that you can go in in different ways to get the same information. I thought it was kind of interesting. I didn’t plan it. It just kind of happened in class.
Music streaming apps (Lyrics for reading, pronunciation and poetic writing)
- Music is such an easy and less intimidating way for people to engage in learning. It gets away from that grammatical imposition of schooling to learn how to write. You can you can pull up the lyrics on any song you know on apps like Apple Music or Spotify. You can play with a song, look at the lyrics and then try to write one verse of a song without worrying about sentence structure–you can get your words down and then move from there to writing a sentence to writing a short paragraph. Or you can create a poem about something and then create an opinion paragraph about why you think a certain way about the topic. You can do this online, digitally, or it can be in person, paper and pencil.
Podcasts (transcripts for vocabulary development, digital skills, reading skills)
- It is learner driven by the topics they are interested in. You can get the podcast on your phone, but by going to the websites you can get more information and some have transcripts of episodes that are good for vocabulary and pronunciation practice.
Digital skills
- This is a program by the Goodwill Community Foundation and Goodwill Industries of Eastern North Carolina. Everything at GCFLearnFree.org is free. There are 125 tutorials on a variety of topics. Most topics are about using digital technology. It is easy to get lost on this site – in a good way – by following links at the end of each tutorial.
- If learners prefer to learn using a tablet, Kindle or smartphone, there are apps available at https://www.gcflearnfree.org/mobileapps.
- There are teaching guides. Here is the technology one: https://www.gcflearnfree.org/gcfteacherguides/technology/1/ . The technology guide includes “eight learning plans you can follow and adapt for instruction in a classroom, with a small group, or with individuals.”
- Some of the tutorial sections are text heavy and some literacy learners may find it challenging to access the information. Some have a video as well as text and some are mostly video.
Fair chance learning (Achievia – Microsoft apps training)
- This is a a government funded program that provides certificates in Microsoft Excel, Word, PowerPoint and QuickBooks.
- I like North Star for assessments. Northstar Digital Literacy tests your computer skills. You can build skills in key areas, and demonstrate your knowledge by earning certificates and badges. Northstar is a program of Literacy Minnesota. You can do free assessments. Under the Build Your Skills there are some free learning modules for Basic Computer Skills; Email; and Microsoft Word.
- Activities from the following list of Digital Skills sites (and more) are also accessible through the Digital Skills Library where they have been indexed and are searchable.
Media literacy
- On this site you can see a film about how the achievements of women in sports go unrecognized in best-of-lists and elsewhere and then submit your own corrections. The project began with a girl searching the internet looking for the greatest sportswomen in the world. Her searches revealed many of the greatest male athletes in the world and all of their achievements, but very few women. She was then shocked to discover that when she did search for the achievements of the greatest sportswomen, many of them were superior to the men she was being served in her search results. It turns out, Christine Sinclair has scored more goals in international football than Cristiano Ronaldo. The Black Ferns have won more Rugby World Cups than the All Blacks. And the USA Women’s Basketball Team has won more than double the world cup titles of any men’s team. The facts say that many of the world’s greatest athletes are women, but the internet keeps saying they are men. The reason for this is simple – the algorithms our search engines use are trained on our human behaviour. And now, the internet has learnt our human bias towards men. It’s a problem we created, but one we have the power to fix.
- Whenever you use the Internet, you leave a record of the websites you visit, along with each and every thing you click. To track this information, many websites save a small piece of data—known as a cookie—to your web browser. In addition to cookies, many websites can use your user accounts to track browsing activity. While this type of browser tracking doesn’t pose a serious risk to your online security, it’s important to understand how your online data is tracked and used.
Informable app from the News Literacy Project
- Test your news literacy know-how with Informable from the News Literacy Project – newslit.org/newslit-nation. You can try out three levels of difficulty in four distinct modes:
- Is it and ad or not?
- Is it news or opinion?
- Is this image evidence of the claim being made or not?
- Is the information checkable or not?
- The app is available for Android and iPhones and you can play as a guest.
CBC Gem Video – You are Soaking in It
- I asked learners to watch and answer questions about “pressure to purchase’ and ‘context marketing’
The video is no longer available on Gem. I cannot find it online anywhere so far. Here is the documentary webpage and press kit.
More recommended resource lists:
- The Educator Network Blended Learning Toolbox
- Curated lists
- Useful apps
- The Open Education Resource Library
- Curation strategies: Curating Resources in Adult Literacy
Thank you Gabfesters for your energy, generosity, wisdom and friendship. With your help, we won’t fall off the learning curve.
We hear about the challenge of embedding digital skills in literacy learning when working with learners who have beginner literacy skills or digital skills that do not meet the requirements of an educational setting.
Visit our Computer Basics Google site to see a collection of resources you can use to to support learners who are trying to “catch up” on digital skills.
You will find a collection of places that support learners with beginner literacy skills who want to learn more about using digital devices and leveraging connectivity for learning.
There are Lessons and Tutorials that you can use as a curriculum, build into your own curriculum or supplement a curriculum you are using as well as Lessons and Tutorials created by Ontario Literacy and Basic Skills programs.
Under the Standards tab we have collected resources to help literacy learners reflect upon and assess their computer skills.
Lots of people know about and use GCFGlobal (GCFLearnFree – edu.gcfglobal.org) resources as a place to send learners and to learn about techy stuff themselves.
Here are some other sites for getting started reviewed on this site:
- Text-based resources
You can read more about these places to learn at the AlphaPlus Computer Basics site under the Lessons and Tutorials tab.
You will find activities from these sites organized by topic at the AlphaPlus Digital Technology Readiness site Table of Contents where you will find some basics (parts of a computer, the mouse and the keyboard, etc.) under Getting Started. The rest of the topics are to help learners get ready for using digital technology for learning.
Activities from these sites are also accessible through the Digital Skills Library where they have been indexed and are searchable.
On April 13, 2023 AlphaPlus hosted our seventh Community Gabfest.
The conversation starter was Digital Inclusion / Digital Justice: what does it mean to literacy programs?
This gabfest follows upon the discussion at Calgary Learns. Susan Lefebvre from Metro Toronto Movement for Literacy (MTML) got in touch to talk about how we can bring this conversation to Ontario.
We explored
- the difference between Digital Inclusion (making sure everyone has the devices and connectivity they need) and Digital Justice (making sure that everyone can experience connectivity the same way).
- what our roles as literacy practitioners are, if any, in each of these domains.
We used a Jamboard to guide our conversation: Wayfinders Gabfest 7 Jamboard.
We started by brainstorming some of the ways that digital technology benefits us and/or the learners we work with. I think this is the fullest Jamboard frame I have ever seen.
We looked at Bill’s story (see below) and talked about diversity of ways we see people using technology skills and literacy skills to navigate the world. We also talked about the assumptions that are made about who uses digital technologies (why and how they use them) and how that ties in with assumptions about who has literacy skills and skills deficit approaches to education.
We talked about what digital inclusion means. We concluded that essentially it comes down to issues of affordability and that as long as the provision of internet access remains a private sector, for profit venture, affordability will continue to be an issue–especially in an era where we seem to moving to more privatization of public services.
When we tried to answer the question about the role of literacy programs in addressing the issue of digital inclusion, as one person said, there was a “startling pause.” It was felt that it though would be quite natural and for people who work in literacy programs to be part of developing inclusion strategies because of their deep knowledge of the impacts and realities of lack of access, program workers are stretched pretty much to the limit. To add on the work of trying to solve a problem that is really one of government regulation and investment, as essential as it is, is just not feasible.
We rounded out the afternoon by grappling with the notion of digital justice. We reflected on Jane’s story (see below) and how access to your data and artifacts is a human right. We talked about how when we work with learners in online spaces, we are often in private spaces. The reason we get to use them for free is because our data and our attention is a valued commodity that gets traded on a market that is largely opaque to most users. People acknowledged that this is the sea we swim in — our ability to change the sea is quite limited but, in this case, there was a lot of energy in the discussion about the role of literacy programs in the digital justice domain. There is a lot we cannot change but we can use our literacy skills, our educator skills and our finely honed critical thinking skills to make the opaque transparent for ourselves and for the learners who are swimming alongside us.
We though that perhaps we could start with language. The jargon of digital spaces and the inconsistent ways language is used in different places and by different people is disruptive to connectivity. For example, are two-factor authentication, two-step verification and multi-factor verification all the same thing or does each term mean something different? Literacy people are language people. People saw ways that they could demystify the language as part of media literacy activities and lessons.
Audrey Gardner recommended a video to us on CBC Gem called “You’re Soaking in It” as a way to make this more understandable to ourselves.
We wrapped up by talking about how to bring this information to literacy learners and how to be transparent about the digital learning environments we are taking learners to. We thought one place to start might be the Media Literacy section of the Educator Network Blended Learning Toolbox.
Tracey and Guylaine were sparking with ideas about other ways AlphaPlus can support the field in this endeavour. More on that soon.
Thank you Gabfesters for your energy, generosity, wisdom and friendship. With your help, we won’t fall off the learning curve.
The Calgary Learns Digital Justice Panel
“A digital justice approach to literacy education asks not if people can access the Internet and digital technologies but rather how different groups experience online worlds.” — S. Smythe and D. Pelan (2019) Digital literacy and digital justice
Here is the link to the video of the discussion panel.
These are the articles we were invited to read before the panel:
- S. Smythe and D. Pelan (2019) Digital literacy and digital justice
- S. Smythe (2022) Beyond Crisis, Toward Justice:New Technologies in Community-BasedAdult Learning
And these links were shared at the event:
- Calgary Learns Digital Divide webpage
- AlphaPlus Digital Inclusion Playbook.
- Metro Toronto Movement for Literacy Digital Literacy Library which includes the resource Accessibility Settings on your Smartphone
- The City of Calgary Digital Equity work
- Design Justice Principles
- Allied Media Projects – Consentful Tech Project
Digital Justice Case Studies
from S. Smythe and D. Pelan (2019) Digital literacy and digital justice
Neil Selwyn (2010; 2014) asks,
“Who benefits in what ways from Internet connectivity?
How does the Internet amplify rather than disrupt existing social patterns and relations?”
(p. 96).
Welfare offices often do not provide help with the application process, nor access to the technology, and so applicants are referred to libraries and community agencies such as tech cafés for help. This requires people to share intimate details about their lives with people they may not know well, an often demoralizing and humiliating experience, and ironically one that people are warned to avoid in the interest of data privacy. The multi-step welfare application process also requires an active email address (and therefore a password and password recovery protocol) and a current digital photo uploaded with the application (requiring a camera, skills to save and upload the photos and so on). The consequence is that people often fail in their welfare applications the first time, moving into deeper precarity.
Google has redesigned its verification protocols to prevent the use of stolen devices and hacking. This is no doubt a positive development for many, but carried catastrophic consequences for Jane, a precariously housed woman who relies on public access computing and who must keep her most precious information on the cloud. Jane lives in a women’s shelter and relies heavily on her Gmail account to communicate with friends, family and work. She uses her cloud storage to keep important photos and documents safe and accessible but does not have her own device, instead relying upon one of the many public computers available in the community. Changes to Gmail’s security features led to flags of suspicious activity because she logs in to multiple computers each day. One afternoon her login attempt at a community centre was flagged as possible “hacking”, with a warning message that because she was logging in from an unknown device she would need to verify that she owned the account before she could access it. Ownership could be verified by a secure access code texted to the phone number she provided when she set up the account or, by verifying the month/year the account was created, then answering the security questions she set up at the time. Jane no longer has access to the cell number listed as the phone was recently stolen, a sadly common occurrence for citizens who stay in shelters. The account was created such a long time ago that Jane could no longer remember the exact month. Indeed, who among us could remember that? After several attempts Jane’s account was locked ‘until she could provide proof’ of ownership. But there were no other options for proving ownership and in those few moments, Jane lost access to her vital documents, contacts, phone numbers, and main method of communication with no way to retrieve them. Such experiences of disconnection are deeply disruptive and traumatizing for those with histories of personal loss and abandonment.
Bill often attends the tech cafés to learn more about how to use his laptop. He is confident and fluent in his online activities and an active participant in social media. One day, Bill brought in a paper-based form for housing and asked if we could help him find it online but unfortunately, the housing provider would only accept hard copies of the application (a rarity indeed)! This caused Bill enormous anxiety. After a brief discussion it became clear that English was Bill’s second language, he did not see himself as a good speller, and he felt that he did not have legible writing. He stated that this made him feel stupid even though he wasn’t. He preferred to do the form online as the computer would correct his spelling and sentence structure. As digital literacy educators and researchers, situations such as this lead us to question the boundaries between print and digital literacies, and linear views of skills that place people in categories of ‘who is ready’ for digital literacy and who is not. For Bill, digital technologies allowed him to overcome the barriers of print literacy, even if the design of the system still posed difficulties.
A Blended Learning Toolbox by and for Ontario literacy educators
As part of the Educator Network Blended Learning program, literacy practitioners share the resources that are most helpful in creating lessons and activities that engage learners and enhance and expand learning.
This is the collection from the Winter 2022 group.
These are the blended learning resources, activities and tools that practitioners have tested and are recommending. On some pages you will see their reviews or tips.
We start with an explanation of some of the terms we used and a link to a website about curating resources.
We have included an index. Some topics have several pages. If you open the PDF in a browser, you can use the back button to return to the index.
Use the link in the sidebar to open and download the collection.
On March 9, 2023 AlphaPlus hosted our sixth Community Gabfest.
The conversation starter was Lori Armstrong’s video The Personal Web.
Lori is a knowledgeable and inventive literacy instructor who currently works at the Thunder Bay Literacy Group and will soon be moving to the Lakehead Adult Education Centre (part of the public school board in Thunder Bay).
In the summer of 2022, Lori participated in the AlphaPlus Wayfinders Maker Space and created a video about the Personal Learning Web – a map of how Lori works with learners to identify the ways connection, relationships and power impact the whys and hows of learning for each of us differently and specifically.
We used a Jamboard to guide our conversation: Wayfinders Gabfest 6 Jamboard.
It was a lively and engaging discussion as usual.
We started by talking about the elements that create good learning. We then watched the first part of the video — the overview of the Personal Web — and moved to breakout rooms to discuss how the web resonated with us and our practice. One group made connections to the issue of digital justice.
We watched the second part of the video and stayed together to talk about how teachers dance with chaos and navigate the web of webs. We all found that the pace and flow of Lori’s video — her calm and encouraging tone — put us into an open-minded and meditative space.
Lori finished the session by walking us through some of the ways she has been expanding the personal web concept.
Lori shared a couple of examples of how she’s been extending her Personal Web reflections lately. She showed us how she
- mapped the Anishinaabe Seven Grandfather Teachings onto the Personal Web and
- explored the ways that ADD might be mapped and how the Personal Web can nurture a conversation about the specific ways different people with ADD can be supported as learners
- uses the personal web to work with groups of learners
The PDF linked below shows some concept mapping for the following:
- Page 1: Understanding / discussing Indigenous cultural values (the example here is the Anishinaabe 7 Grandfather Teachings, which I have worked with in a few of the local high schools and adult education programs for Indigenous students).
- Page 2 and 3: Understanding and supporting learners affected by ADHD. I have been researching this because it is such a prevalent condition among my learners and also in my family and community. I have also recently been gob smacked to discover that I am an ADD-affected person, as well.
- Page 4: A simplified think/plan tool that might be used by an individual to prioritize activities for a class, a day, or a week.
Thank you Lori for sparking this good conversation and for your generosity in sharing your research and insights with us.
Thank you all Gabfesters for your wisdom, experience, knowledge and, most of all, your fine collegiality.
We agree with this participant: “Brilliant!! Incredible learning, thank you so very much! Always a pleasure.”
On February 9, 2023 AlphaPlus hosted another in our series of Community Gabfests.
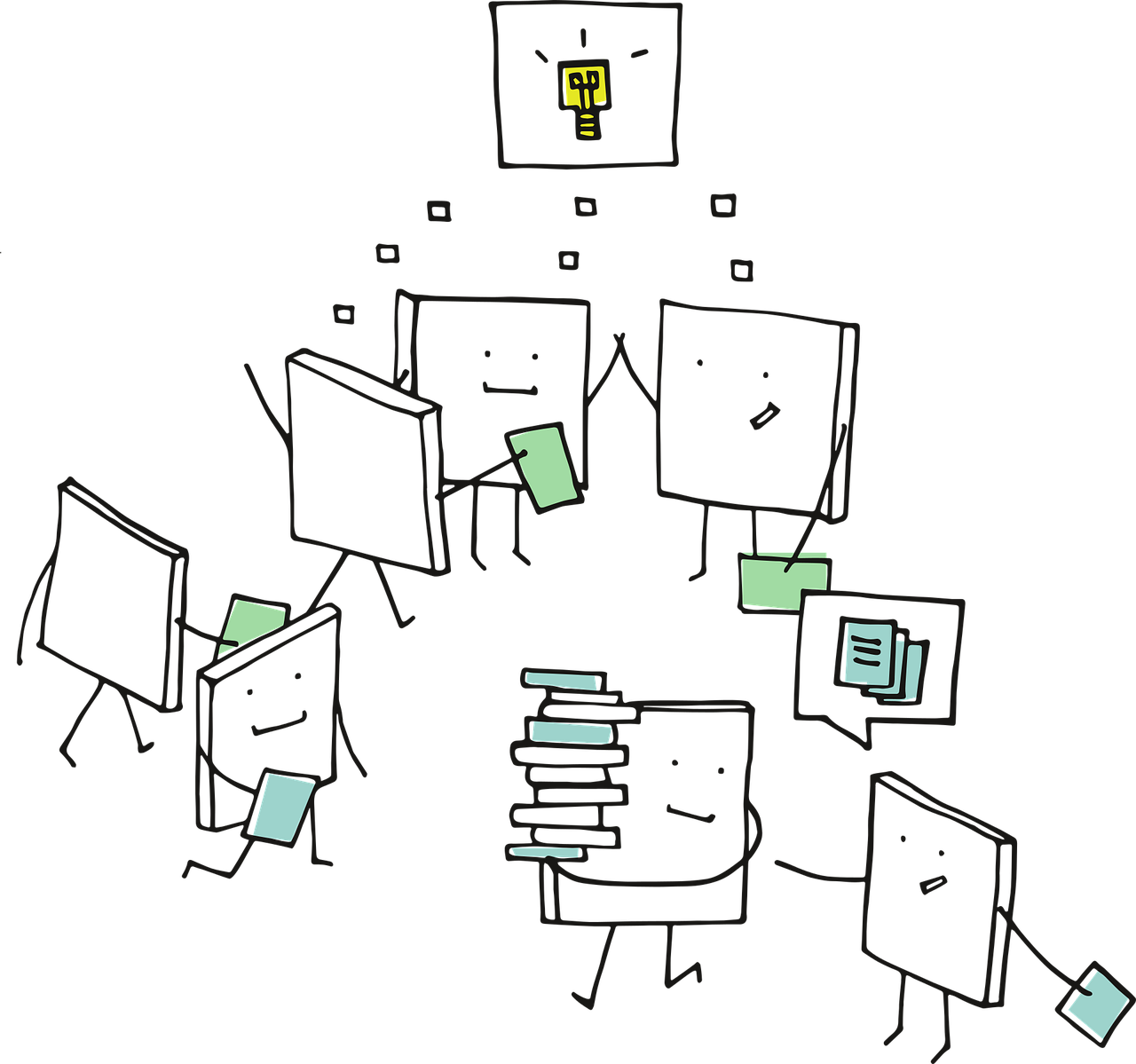
We started by asking people about where they like to learn best.
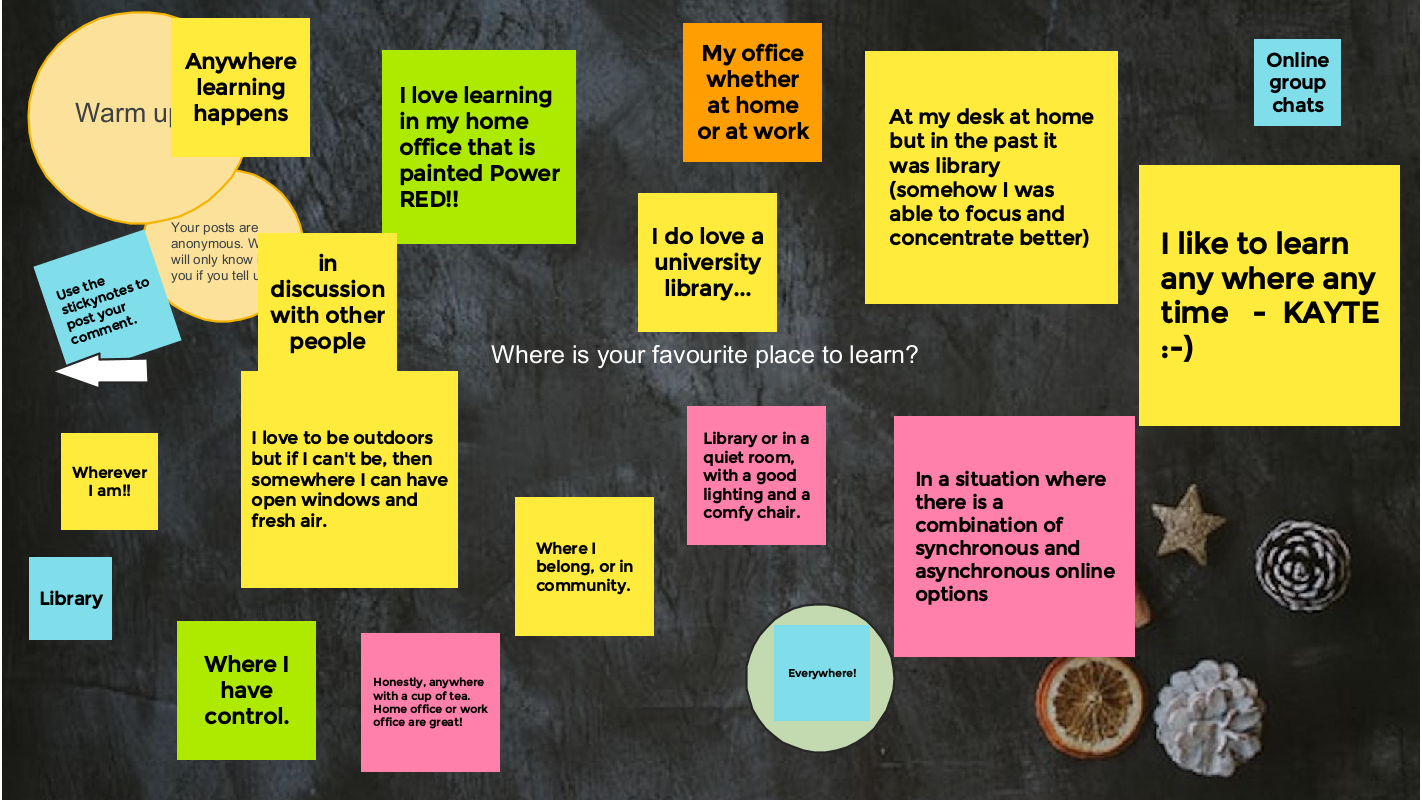
The conversation starter was: If there were no barriers to running a program, what program would you want to run?
We talked about
- If you had the freedom to create your ideal learning place, what would it be like?
- If learners had the freedom to create their ideal learning place, what would it be like?
- How does the tension between dreaming big and working within the constraints of reality strengthen and/or weaken programming?
We moved into break out rooms to discuss the three questions.
Here is what the groups shared on the Jamboard.

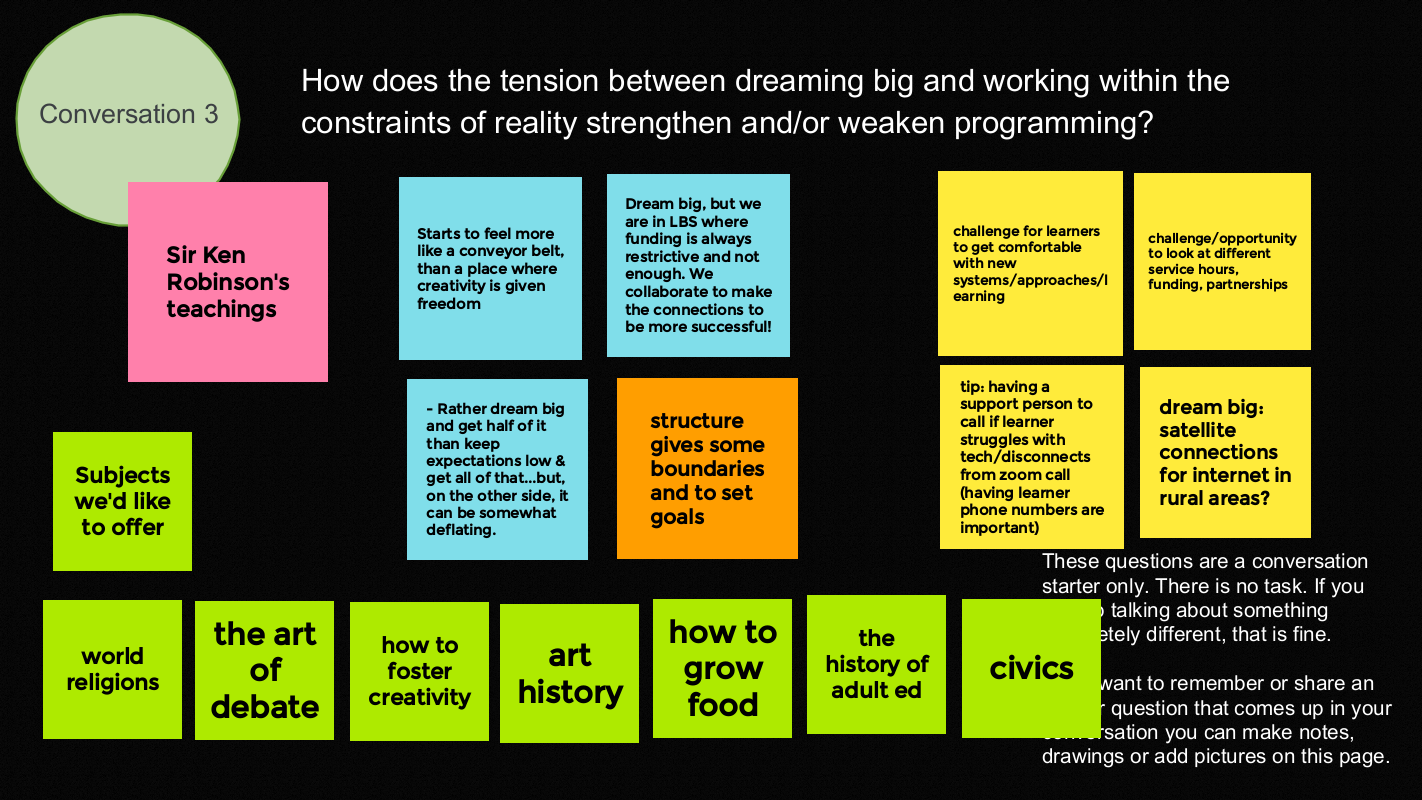
We wrapped up by thanking each other for their contributions and generosity.
- Amazing session everyone. Thank you for your ideas and support!
- What a creative group of problem solvers.
- The enthusiasm is encouraging and infectious.
- Being with people who understand what we do is invigorating.
- Has anyone suggested changing the name? The word ‘gab’ gives me a connotation of idle chitchat, which doesn’t reflect the inspiring conversations that occur. Maybe Community Conversations, or something…
On January 12, 2023 AlphaPlus hosted another in our series of Community Gabfests.
We started by asking people to share the things that they were proud of from 2022.

The conversation starter is: New Year’s Blended Learning *Aspirations
We talked about
- what is going well
- what we are proud of from 2022
- what we want to try next
- who / what could help us
*not Resolutions – the things that are still in dreams, wishes and ambitions phase of planning.
We had a an amazing conversation about
- what went well in 2022
- the specifics of what it means to start where learners are at when we include digital technology as part of that
- the challenges of supporting learners and reducing barriers to learning in the marketplace of apps and devices
- what educational technology we are using and how it is working
- we shared ideas about what technology we want to use and people in the group who were already using that technology shared their expertise
- Smartboards and hyflex and hybrid learning – where some learners are in the bricks-and-mortar classroom and some are connecting remotely – and how people are making it work
- bite-sized learning and byte-sized learning (examples: Skillswise and Rumie)
- the AMAZING Metro Toronto Movement for Literacy Smartphone project
- the changing definition of blended learning and how do we know we are doing it
- how to create independent learning modules, or bytes, in an emergent curriculum context and could H5P be part of the solution
- who used the Winter Break H5Ps in their class 🙂
It was inspiring and interesting.
We wrapped up by thanking each other for their contributions and generosity.
- It is amazing to work with people on their learning adventure!
- Thank you so very much everyone. Your inspiration is great!
- Thanks so much for sharing all your wonderful information
- Thank you for inspiring us!
- Thank you for the excellent ideas and resources!
On November 24, 2022 AlphaPlus hosted another in our series of Community Gabfests.
We started by asking people to share the things that people love about them.

Our conversation starter was: Learner identity (and blended learning)
Here is what Wayfinder Evan Hoskins said:
Each learner has a connection to the past to be considered. All teachers know … every student comes to learning with a different backstory … and you have to know how to adapt your teaching methods quickly. For example, one day we’ll be talking to a learner about how they learn while dealing with anxiety. On another day we will have to talk about what happened in their world before they dropped out of high school in grade nine. What made them not feel comfortable on the computer? We as teachers learn how to help the learner work through that emotional pain in order to gain the confidence needed to learn how to use the computer, to get their fingers moving again.
What do you think? How do you navigate this terrain and support learners as they develop their learner identities and confidence?
We had a an amazing conversation about
- what we need to know about people so that they can thrive in literacy programs
- how working with learners is an iterative process of experimentation and discovery as literacy facilitators work to find the learning environments that work best for each participant
- the challenges of supporting learners and reducing barriers to learning while mapping boundaries and expectations
- the challenges of nurturing our own mental health and staying energized so we can do the work that we love
- how pandemic recovery is about more than economic opportunities and assessing where we are in terms of digital technology integration
It was a lot. And it was inspiring and validating.
We wrapped up by thanking each other for their contributions and generosity.